QUALITY
Quality
When it comes to quality, Schrag knows no compromises. In our plants, we use only the best quality materials from selected and proven suppliers.
We provide our clients with the best. To do this, we uncompromisingly focus on quality. At all Schrag plants in Europe, we use state-of-the-art numerically controlled machine tools.
Types of steel
The following steel grades are used in the production of cold-formed sheet steel parts: DX51D + Z 275 MA-C, S350GD, S390GD, S450GD acc. to PN-EN 10346: 2015, S235JR acc. to PN-EN 10025-1,-2:2007, S355MC acc. to PN-EN 10149-1,-2:2014, DD11 acc. to PN-EN 10111:2009.
Dimensional accuracy of the thickness of manufactured sections from 0.50 mm to 3.00 mm – acc. to the following standards: PN-EN 1090-4: 2018, PN-EN 1090-2: 2018 “Cold-formed steel sections. Technical requirements for deliveries. Dimensional and cross-sectional tolerances.”
Dimensional accuracy of the thickness of manufactured sections 4.00 mm – according to individual arrangements.
In addition, we also manufacture sections of aluminium, stainless steel and acid-resistant steel sheets.
Protective coats
Metallic coats
In order to protect cold-formed steel sheets against corrosion, metal coats are applied on both sides by hot-dip galvanizing in a continuous manner. The selection of the appropriate system of protection against corrosion must be matched to the technical requirements. In particular, we recommend taking into account the provisions of DIN 55928 -8[3], DIN 18807 -1, PN-EN ISO 12944 -1, -2, [1], [2], PN-EN 10169 -1, -2 , -3 [8], [9], [10], and technical guidelines.
The following metal coats have proven themselves in the construction industry:
Zinc (Z 275)
- The coating consists of a layer of zinc containing at least 99% of zinc by weight. With 275 g/m² zinc coating on both sides, this corresponds to a layer thickness of 20 μm per side
- K I protection against corrosion (both sides)*
- Zinc coating properties: better resistance to corrosion and the deformability, longer period of protection against corrosion, the formation of white rust is possible in humid environments without air circulation
Zinc-Aluminium (ZA 255), Galfan®
- The coating is an alloy consisting of zinc with the addition of 5% of aluminium and 0.05% of other metals
- K I protection against corrosion (both sides)*
- Coating properties: adheres particularly well to organic layers, aluminium increases the passive protective effect
Aluminium-Zinc (AZ 185), Aluzinc, Galvalume®
- The coating is an alloy consisting of 55% of aluminium, 43.3% of zinc and 1.6% of silicon. With the application of 185 g/m², this corresponds to 25 μm per side
- Protection against corrosion K III (both sides) when 185 g/m² is applied*
- Coating properties: excellent resistance to corrosion especially in acidic atmosphere, high resistance to scratching, good resistance to heat and excellent heat reflectivity
Organic coats
Undoubtedly, in order to improve the resistance of the galvanized sheet to corrosion, there is an additional possibility of applying an organic coating. It is referred to as the so-called duplex system. In addition, the organic coating on building elements and sections performs an aesthetic function. As a rule, the coating is applied in a continuous process to a metallic carrier (coil coating). The types of organic coats used are liquid, roller-applied duroplastics, thermoplastics and polyfluorovinylidene (PVDF), which are cured in the furnace at the final stage of the process. In addition to the aforementioned wet coats, there are also film coats. In this case, a coloured film (e.g. PVC or PVF) is applied to the steel sheet.
The choice of the appropriate coating system definitely depends on the standards of protection against corrosion, deformability, resistance to temperatures, required colour and degree of gloss, as well as surface hardness, etc. In order to meet the wishes regarding the colours, in addition to the possibility of using a coated material applied in a continuous manner, structural elements can be powder coated or wet coated after production.
The following materials are used for outdoor applications:
Polyester (SP), 25 μm / varnish on the underside
- Coat thickness approx. 25 μm (also possible on both sides 25 μm)
- Protection against corrosion, top side K III, underside K II
- Properties: cost-effective coating with satisfactory resistance to weather conditions and abrasion, good deforamability, temperature resistance up to max. 80°C
DU/DU (SP) polyester, 10 μm varnish on the underside
- The layer thickness of this thin coating is approx. 10 μm
- Protection against corrosion, top side K II, underside K II
- Properties: reduced resistance compared to the 25 μm polyester coating
Polyurethane (PUR), 25 μm / varnish on the underside
- Coat thickness approx. 25 μm
- Protection against corrosion, top side K III, underside K II
- Properties: similar to polyester (SP) one, very good deformability, sufficient resistance to abrasion
Polyvinyl chloride – Film, PVC (F), 100-200 μm / varnish on the underside
- The thickness of this film system is between 100-200 μm, depending on requirements
- Protection against corrosion, top side K III, underside K II
- Properties: similar to PVC plastisol
Polyfluorovinylidene (PVDF), 25 μm / varnish on the underside
- The thickness of the coat is 25 μm
- Protection against corrosion, top side K III, underside K II
- Properties: good and very good deformability, resistance to UV rays, chemical resistance, good resistance to abrasion and high surface hardness, the highest quality level among 25 μm coats applied by continuous method, high thermal load capacity up to +110°C.
Polyvinyl chloride, Plastisol, PVC (p), 100-200 μm / varnish on the underside
- The thickness of this liquid coat is between 100-200 μm, depending on requirements
- Protection against corrosion, top side K III, underside K II
- Properties: good deformability, the resistance to weather conditions is strongly dependent on UV radiation, exposure to temperatures above 60°C should be avoided
Polyvinyl fluoride – Film, PVF (F), 100-200 μm / varnish on the underside
- The thickness of this film system is approx. 40 μm
- Protection against corrosion, top side K III, underside K II
- Properties: comparable to PVDF coating. These types of films are offered only in a low gloss version and in a limited choice of colours. In addition, we can offer the delivery of sections coated with PVC spray (30-80 μm) or powder coated with polyester (60 μm), in special colours or in case of small batches.
Corrosion and protection against corrosion
Thanks to the metallic coating steel sheet is protected twice:
- passively, through a barrier effect, by a densely adhering coating layer
- actively, by cathodic protection of zinc-coated steel, in case of damage to the coating and on cut edges.
The passive protective effect is increased by the aluminium content in the alloys. With additional organic continuous coating, a barrier effect occurs because the polymer layer is impermeable to ions. In open-air tests with hot-dip galvanized sheet, the following values of spontaneous zinc coating loss were determined:
| Environment | Annual loss in μm |
| Country air | 1,0 do 3,4 |
| Sea air | 2,4 do 15,0 |
| City air | 1,0 do 6,0 |
| Industrial air | 3,8 do 19,0 |
Cathodic protection
The property of zinc, referred to as “cathodic protection”, consists in the negative, compared to iron (steel), assignment of zinc in the so-called electrochemical voltage series.
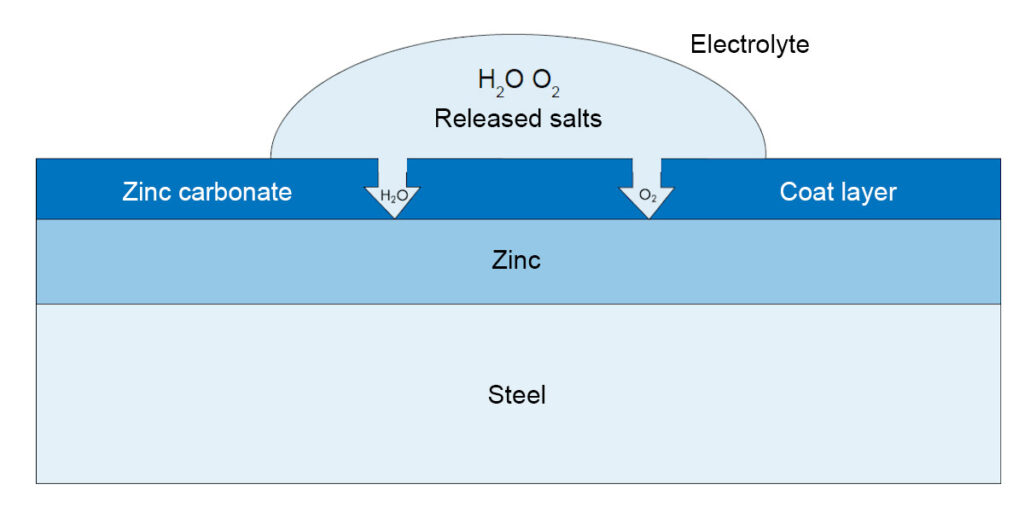
Barrier effect provided by a densely adhering coat layer
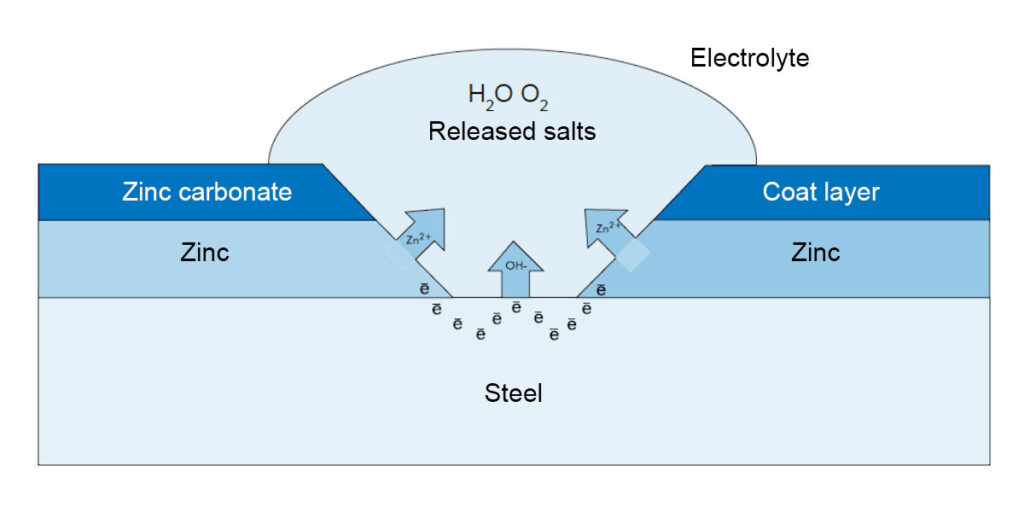
Cathodic protection of steel
The cathodic protective effect takes place only when the two metals zinc and steel are connected to each other through an electrolyte (condensate, rain, etc.) and, conducting an electric current, form an electrolytic cell. On cut edges and in case of damage to the zinc coating, the steel core is exposed. The added moisture acts as an electrolyte, a galvanic cell is formed, resulting in a voltage difference between the metals. Zinc, as a less noble metal, enters the solution as an “anode”, i.e. there is a migration of electrons from zinc to steel. As a result of this process, the exposed surface of the steel is covered with zinc atoms and is protected against corrosion. This phenomenon is shown in the photo above.
Many years of experience in the use as roof and wall elements (sheet thickness 0.55-1.25 mm) have shown that corrosion on the cut-off surfaces is insignificant. The experience of professional processing sheet metal shows that red-brown discolouration of cut surfaces is possible, in particular with sheet thickness above 1.25 mm, while the functionality of such elements remains intact and cannot be treated as a defect. When choosing the optimum system of protection against corrosion, the time of such protection is of decisive importance. The period of resistance to corrosion is defined in DIN 55928, part 8. This is the period of time during which the system of protection against corrosion fulfils its protective function. As a rule, it is assumed that the protection period is exceeded if more than 5% of the sheet surface shows signs of disintegration of the base material. Such features include the occurrence of white rust, the disappearance of the coating on cut surfaces, damage and the occurrence of scratches together with pealing of the coating. Such phenomena can be regarded as advanced corrosion combined with reduction of the base material with possible risk of rusting. Maintenance is necessary to avoid loss of base material. Such effects as loss of gloss, chalking, change in colour shades indicate the beginning of the decay of the organic coating, thus affecting the aesthetics of the building, but they do not pose risk to the safety of the profiles.
White corrosion
It forms as a result of contact of a freshly galvanized surface with moisture in the form of fog, frost, rain or snow, when such freshly galvanized surfaces have not yet managed to develop a protective layer of zinc carbonate patina and have already come into contact with moisture. Zinc corrodes in all conditions, and with high air humidity, this process is accelerated.
The name “white corrosion” comes from the white colour of the corrosion products deposited on the zinc surface, constituting a powder coating, easy to remove in the initial phase. It consists primarily of zinc oxide and zinc hydroxide.

White corrosion spoils the appearance of galvanized steel, but does not reduce its resistance to corrosion. The main component of white corrosion, i.e. water-insoluble zinc hydroxide crystals, settling directly on the surface of the sheet, forms a coating that inhibits further reaction of zinc with oxygen contained in the air and partially protects the zinc against corrosion. The emerging spots of white corrosion should be controlled and, if possible, removed, because the lack of ventilation and the possibility of drying of the galvanized product may result in the lack of the protective layer, and eventually corrosion will expose the surface of raw steel.
Storage of sections
Sections are a product sensitive to corrosion and damage, therefore, in order for our products to be of the highest quality, special care should be taken to protect them properly, both against corrosion and against mechanical damage.
Sections made of galvanized steel sheets should be protected against weather conditions (humidity) during storage. They should be stored under a roof or covered with tarpaulins, ensuring good ventilation (plastic foils have not worked and are not used in this purpose). In order to ensure good ventilation, remove the fastening tape from packages or pallets with sections. Moisture between the galvanized sections causes the formation of initially white and then red rust in the electrolytic manner. To prevent penetration by moisture, storage should take place on a stable, slightly sloping surface, then any water that has penetrated inside can easily be drained. Contact with the ground must be strictly avoided. It should also be ensured that the distance between the floor and the edge of the package is at least 30 cm.
|
Sections made of galvanized steel and aluminium coated with polyester (except for the DU coating) are prepared and delivered with a one-sided protective foil, which must be removed immediately after assembly. Before the assembly process, the sections should be protected against sunlight. The impact of sunlight can make the protective film permanently stick to the paint, which may cause the paint to peel off from the substrate upon the film removal, thus damaging the paint coat.
Production
As a leading expert in the field of production of sections made of surface-refined steel sheet, in our plants we offer you solutions in the field of the following product groups:
Sections for roofs and walls
Attics, attic corners, gable elements covering the roof sheathing, drip caps, wall corners, window and door frames, wall coverings, coffers, substructures, etc.
Lightweight steel beams
Purlins, wall transoms, bases for skylights and smoke vents, roof replacements, basket gutters, etc.
Special profiles
Profiles for storage racks, containers, gates, silos, etc.
Special profiles according to design or pattern
Materials
Galvanized steel (0.50-4.00 mm), galvanized/coated steel (0.50-2.00 mm), aluzinc (1.00-2.00 mm), aluminium (1.00-3.0 0 mm)
Technological possibilities
Sheet metal unrolling and drilling, cutting (elements up to 8000 mm long), punching holes (elements longer than 16000 mm). Additional services for complete profile processing:
- punching
- mechanical cutting
- drilling holes
- riveting
- welding
Advantages
- the expertise of our employees
- the high quality of the offered products – our plants are equipped with the state-of-the-art CNC-controlled machines
- many years of experience in the production of cold-formed sections
- cost-effective preparation in industrial conditions
- 8,000 tons of material stock, which enables fast deliveries.
Our production facilities guarantee you a wide supply of cold-formed sections, according to our motto:
- reliability
- speed
- quality

