WELDING AND RIVETING
Our services
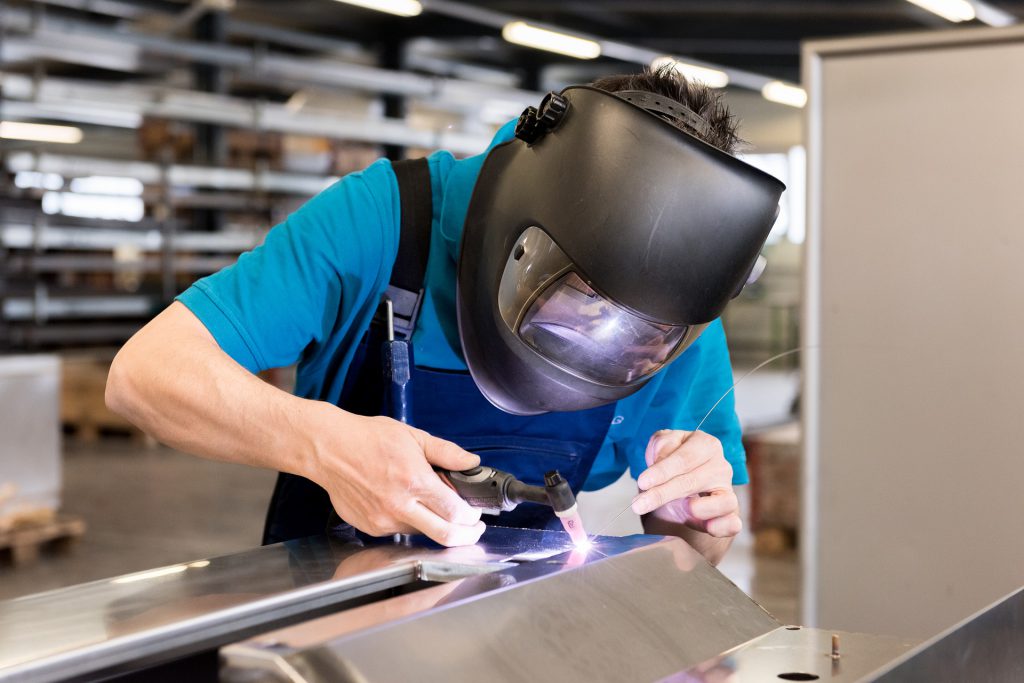

Welding
In addition to bending or drilling holes, we also weld steel elements made by us. Welding consists in permanently joining of materials (mainly metals and their alloys) by heating and melting them at the joint with or without the addition of a binder. In this process, the heat source is usually the welding arc.
Elements that are very often subjected to this type of processing include: inter-purlin braces, façade substructure elements, basket gutters.
Types of sheets that we weld:
- Hot-formed steel (the so-called black) (S235, S355)
- Galvanized steel (DX1D, S350GD, S390GD)
- Aluminium
The classification of welding methods is made on the basis of the method of generating heat as well as the feeding of additional material. The selection of particular technique depends on the welded material and its thickness, the desired aesthetic values and the target quality of the weld. Due to the fact that the welding process is associated with a number of risks, it is performed in a specially adapted room by experienced and qualified personnel.
We offer MIG ( Metal Inert Gas), MAG ( Metal Active Gas) and TIG ( Tungsten Inert Gas) welding.
MIG/MAG welding is usually listed together, which is why many people think that it is the same method. Nothing could be further from the truth. Of course, there is a lot of similarity between them. Both are arc welding techniques, and both are performed in a gas shield with a consumable electrode.
The main difference between MIG and MAG is the type of gas used. During MAG welding, active gases such as pure carbon dioxide or a mixture of gases (argon, oxygen, carbon dioxide, helium) of various compositions are used. The MAG method is used to weld high-alloy, low-alloy and non-alloy materials.
MIG welding uses inert (non-reactive) gases such as pure helium and argon or mixtures of helium and argon. This process is suitable for welding non-ferrous metals.
TIG welding also consists in creating an electric arc, but it is produced by a non-consumable tungsten electrode in an inert gas shield, usually helium or argon. It protects the electrode and weld against oxidation. The TIG method is used where the highest quality of the weld without spatter is necessary. Undoubtedly, it is perfect for joining stainless steel, aluminium and nickel alloys.
Riveting
Riveting is the oldest and at the same time the easiest way to permanently connect two independent structural elements using rivets. What exactly are rivets? These are metal elements in the form of a cylinder, e.g. made of steel or aluminium.
At present, classic rivets have largely been replaced by blind rivets. What is the difference between them? A classic rivet has the form of a short rod, which ends with a head on one side and a hook on the other (the latter part is beaten during riveting). A blind rivet, on the other hand, consists of two parts – a sleeve and a rod. The name of this rivet comes from the method of riveting. During the joining of materials, the wire is detached from the entire rivet.
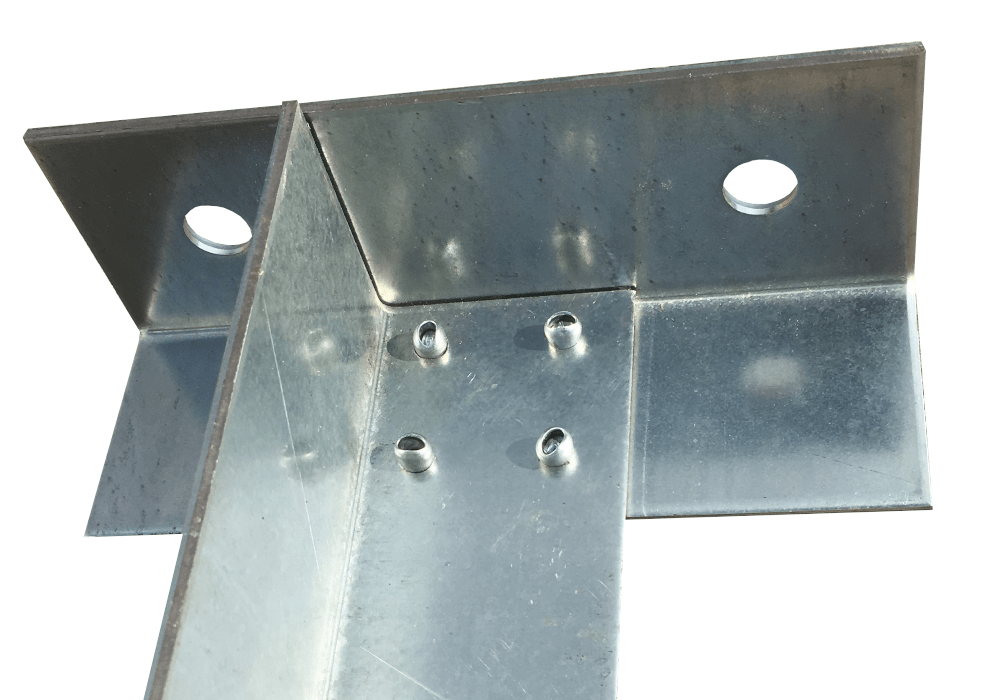

Blind rivets can be grouped according to:
- type (closed, forked, expanded),
- head shape (flat, enlarged, recessed),
- application (universal, for soft materials, resistant to vibration and high pressure),
Riveting was popular before welding techniques were invented. In principle, riveting is still an alternative to welding, especially when it is important to obtain quick results of work or if welding structural elements is not possible. Thanks to this solution, we are able to deliver elements ready for assembly to the construction site.










